Last Updated on February 27, 2025 by maximosecrets

Topics

Good morning, I’m Andrew Jeffery and I’m pleased to be giving you an introduction to Maximo Asset Management
We’ll start by looking at what Enterprise Asset Management is and we’ll have a look at an Asset Management Maturity model
We’ll then turn our attention to answering the question “What is Maximo?” We’ll do that by looking at the Maximo Product Portfolio and exploring the core Maximo modules and some add-ons that help to move a client along the path to greater asset management maturity
Finally we’ll look at some trends in Enterprise Asset Management and what the IBM team are doing to ensure that Maximo continues to be recognized as a leader in this field
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)

So lets get started with answering the question “What is Enterprise Asset Management?”
There are many types of physical assets both fixed, for example plant or process equipment, and buildings, or mobile assets, for example, vehicles like trucks and vans, mobile cranes or medical devices. Enterprises will find they have multiple physical asset types and in multiple locationsA physical place where assets exist and where work can be performed. More around the world. Hence, Enterprise Asset Management, is the management of all of these physical asset types of an enterprise, no matter where they are.
The physical asset types within one enterprise can be very different and so the management of those assets can also differ across the enterprise. For example, the management of infrastructure assets in electric transmission or distribution, is quite different from the management of assets in a power plant or wind farm that generates the electricity.
Physical assets exist in every industry imaginable. The management of assets in a manufacturing plant is very different from those in a cement plant. Asset management in pharmaceutical companies, utility companies, facility management companies, airports, train operators or train infrastructure companies have some similar foundational needs, like work management and the need to handle inventory parts for asset repairs etc, but those needs can be quite diverse.
Maximo is used by clients in every industry with physical assets and has a range of functionality that you will find out about. In all of these industries there are some value drivers that a client is wishing to gain from its asset management system, like reducing unplanned downtime, maximizing resource usage, or reducing inventory costs. Some Maximo clients will be looking to comply with asset management standards, for example PAS55 or the ISO 55000 standard.

An Asset Management Maturity model is used to describe where a company exists in relation to the top performing enterprises. The asset management maturity model has evolved over the years as technology has advanced. It used to be Reactive, Preventive, Condition based, and Predictive. But the boundaries between Enterprise Asset Management and Asset Performance Management are overlapping and Risk based, Prescriptive and Cognitive are being added to the latest maturity models. The basic premise is about understanding strategy, people, process and technology – NOT just technology alone.
Those starting out on their journey towards operational excellence view EAM as a cost, and maintenance as a cost center, whereas more mature organizations view EAM as a service center, and operational excellence is driven through close collaboration between operations, maintenance and engineering. As organizations mature, maintenance then shifts from being viewed as a necessary expense through to an investment which creates business value.
As you look at the model, or move from the bottom left to top right, overall maintenance costs can be reduced but the value to the organization as a whole increases as assets become more reliable, downtime is reduced and asset performance is increased. The move up the Asset Management Maturity model is enabled as assets become more instrumented and interconnected through IoT based platforms like IBM Watson IoT Platform. This rise in available data “big data” is of no use unless you intelligently make sense of it through analytics and optimization. But analytics and optimization can be performed on existing data if data quality is sound, you needn’t instrument the assets first.
The Asset Management Maturity Model displayed here has five levels, your starting off point may not be at the beginning. Remember though that moving through to successive levels in the maturity model will take time and effort and a commitment from all stakeholders. Additionally, not all assets are the same, for some it will be quite acceptable to replace them when they have broken, for others we might listen to the assets for audible or inaudible changes in order to predict future failure. You cannot move direct to Advanced level without moving through the other stages and deciding what asset strategy is applicable, asset by asset.
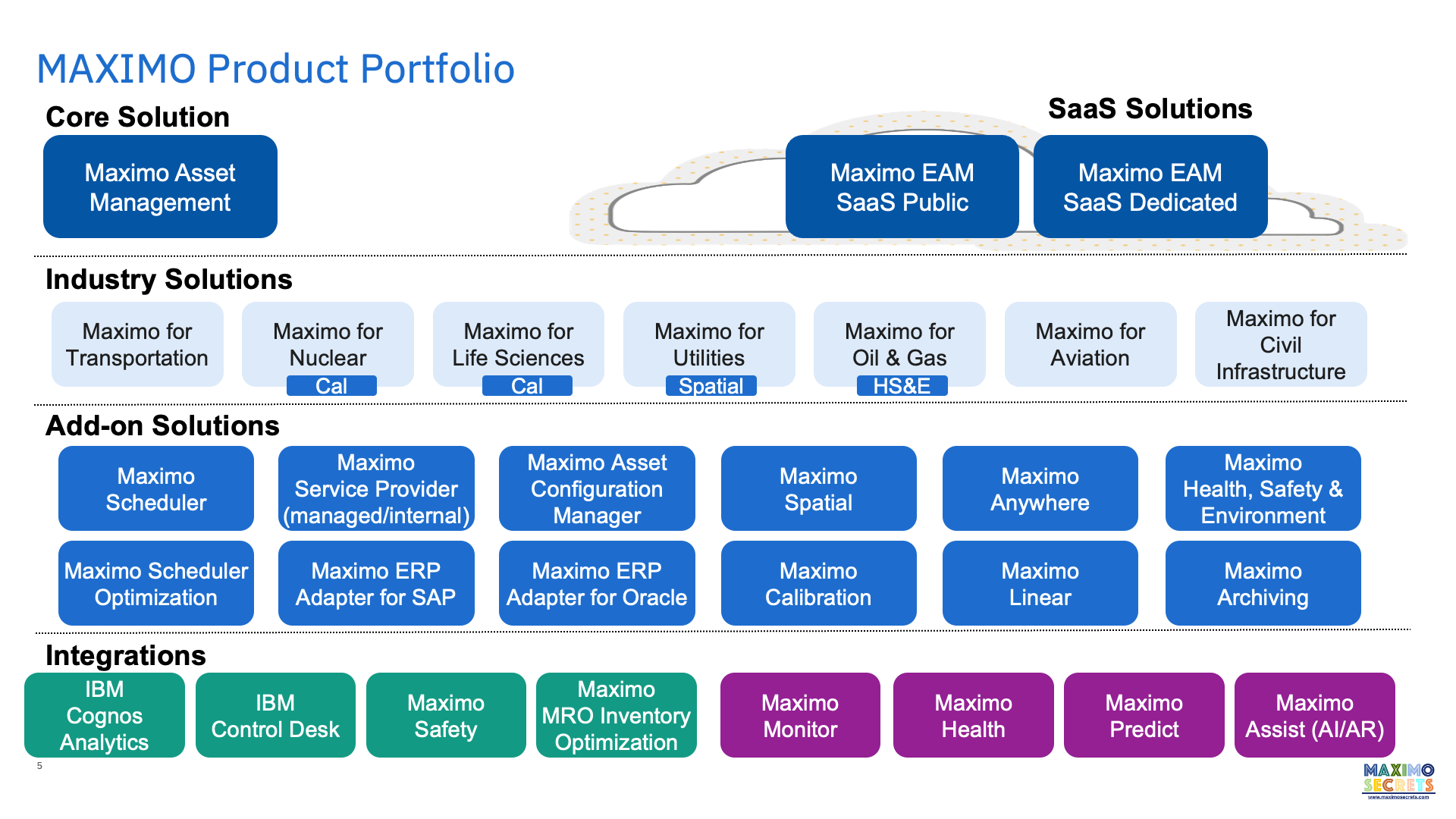
Product Portfolio

Maximo is a broad portfolio and suite of offerings designed to meet the needs of Enterprise Asset Management clients, across multiple markets and asset intensive industries. Maximo is available as both on-premise and cloud based.
Maximo is extended with industry solutions; Civil Infrastructure is the latest of these. Each industry solution has a focused team and unique roadmap, driven by customer development partners and market demands.
Add-on solutions further extend the capability of Maximo and some are included in some of the industry solutions.
- Maximo Scheduler is a range of graphical based scheduling and assignment applications providing Gantt based long- to short-term scheduling, assignment and dispatch of crews and labor to work, asset-based scheduling, appointment scheduling, crew management and resource management.
- Maximo Scheduler Optimization uses the IBM Maximo Optimization Framework for running schedule optimization models developed in IBM CPLEX Studio. Models are provided for capacity planning, resource leveling, labor assignment and spatial scheduling.
- Maximo for Service Providers is used where there are external or internal customers where the billing of work or usage/lease of assets is required.
- Maximo ERP Adapter for SAP and Oracle provide a set of integration points including for SAP S/4HANA. For integration to other finance systems the Maximo Integration Framework (MIF) is used, this is a part of core Maximo.
- Maximo Asset Configuration Manager is for the management of complex assets, particular those which may get maintained by different parties and where there is a need to understand the differences overtime between as-designed and as-built, it is mainly used by aviation and train companies.
- Maximo Spatial is the integration or rather the embedding of ESRI’s ARCGIS in Maximo. It allows users to plan work in a spatial context. Base Maximo also has mapping capability using Google or Bing maps.
- Maximo Calibration is used for instrument calibration, there is a mobile version of this as part of Maximo Anywhere.
- Maximo Anywhere is a suite of mobile applications (10+) which are broadly based around asset, inventory and work order processes. Most of them work in offline mode as well as online.
- Maximo Linear is used for roads, railways, cables and pipes where the characteristics of the asset changes over a measured distance and where maintenance must be performed at a particular point or part of the asset.
- Maximo Health, Safety and Environment Manager (HSE) is a very large suite of additional applications and functionality added to core Maximo applications which extend Maximo towards meeting ISO 55000 standards.
- Maximo Archiving is an archiving solution for the transactional records of Maximo like work order and ticket.
Integrations
A Maximo client is entitled to use IBM Cognos Analytics 11.0.13 for reporting, dashboards and business intelligence, but only against the data held in the Maximo database.
IBM Control Desk (ICD) is an additional suite of applications and integrations for managing IT assets including software licenses. It has deeper service desk functionality than Maximo and is sometimes used by Maximo clients who are not managing IT assets; facility managers and communications providers.
Maximo Safety previously Maximo Worker Insights is a product that integrates sensors in wearables that monitor health and wellbeing, as well as proximity safety, tracking a worker who has entered or is approaching an unsafe area (very relevant currently).
Maximo MRO Inventory Optimization is a cloud-based suite of optimization models and analytics for storerooms including, inventory optimization, lead-time analysis, critical spares analysis, demand forecasting, and what-if analysis.
There are four Asset Performance Management (APM) products in the Maximo family called Maximo Monitor, Maximo Health, Maximo Predict and Maximo Assist.
Maximo Monitor is an AI-powered remote monitoring product that monitors operations and sensors and creates fewer and more accurate alerts giving insight into what is causing asset failures, it can do this at scale across the enterprise. It leverages the platform and analytics services of IBM Watson IoT Platform.
Maximo Health was known as Maximo Asset Health Insights (MAHI). It is focused on the needs of the Asset Reliability Engineers and supports condition-based maintenance (CBM), repair/replace decisions and asset health scoring. It also has an integration to Maximo Predict.
Maximo Predict was known as IBM Predictive Maintenance Insights. It is a cloud-based system for PM optimization and predicting the end of life date for an asset. There are five out-of-the box predictive models.
Maximo Assist was known as IBM Equipment Maintenance Assistant. It is a system that can ingest structured and unstructured data from many sources to provide optimized repair guidance. It uses AI powered continuous learning and natural language processing. It is the product that would most address the issue of a loss of knowledge through an aging workforce. There is a remote assistant element to this which operates from the Work Execution work center.
Asset Management

At the core of Maximo is the Locations and Assets applications. Locations can exist in multiple systems both hierarchical and network, a location in a network system can have multiple parents. A location can have a service address which defines the latitude/longitude of the location and positions the location on a map. All locations and assets below this in the hierarchy will have the same map position.
An asset exists at an operating location or it may exist in a storeroom waiting to be issued. Assets may have an asset hierarchy and/or a set of spare parts. Fixed assets are commissioned at their operating location and do not move until they are decommissioned. Some assets are termed rotating, meaning that we track the asset from the storeroom to the operating location then to the repair shop before it is returned to the storeroom again for issue to another operating location.
Linear assets (roads, rail, pipelines and cables), mobile assets (plant hire, tools, medical equipment), and transportation assets (trucks, vans, buses, trains) can all be handled in Maximo. Linear assets is an optional add-on product and it uses Relationships and Features to define how linear assets relate to each other and the features that exist along the path of the linear asset. Relationships can be used to define any relationship between two assets, not just linear ones.
The characteristics of locations and assets are defined by a classification hierarchy and a set of attributes associated with each class. Classifications can be used for purchased or stocked items and many other record types in Maximo, for example Service Requests or Work Orders. The descriptions of classifications and their attributes can be made multilingual.
Assets can be generated from Asset Templates. The asset template has a classification, may have multiple meters and spare parts, and associated Master Preventive Maintenance records that define how the asset will be maintained, inspected or monitored. Meters are continuous (runtime), gauge (measurements) or characteristic (observations). The meter values can determine when preventive or corrective work is performed. The Condition Monitoring application is used to receive the measurement made against assets and meters of type gauge and characteristic and to raise a work order when they exceed limits.
Finally there is a Failure CodesFailure Codes exist as part of a Failure Hierarchy and are a Failure Class, a Problem, Cause or Remedy Code. More application for defining failure classes and the problem, cause and remedy codes used in failure reporting on a work order.
Inventory & Logistics

Maximo has three types of items and hence three main applications for recording them, Item Master, Service Items and Tools. The characteristics of an item can be described using a classification and the attributes of the classification, the specification. The classification and attribute values can be used to generate the description of the item, this can create a lot of consistency in your data. Users will find lookups which allow you to perform word searches, or searches based on the classification hierarchy or an attribute based search. The item can have an image and like all Maximo applications document or URL links can be associated with each record.
Items and tools can represent both consumables and items for which assets will be recorded, rotating items. Like items can be grouped using commodity groups and codes. Items can be condition enabled meaning that multiple records can exist for the item but at different values. For example, a new tyre for a truck has a different value to one where the tyre is worn by 20%. Items can be kitted meaning that several items are assembled into a kit of parts waiting to be issued as a whole. Items can also have an item assembly structure, and this is used with assets to quickly build an asset hierarchy and its spare parts. There is also a setting to add an item to the asset spare parts whenever it is used on an asset.
The Inventory application is where balances of the item can be held in a storeroom. The Stocked Tools application is the equivalent storeroom application for tools. In the Inventory application balances can be held for the same item in multiple bins. The balance of items can also be held at the lot level which would be used for chemicals and paints with a shelf life. Item balances can also be recorded against people, for example the custodians of tool assets, and transit locations like couriers and shipping/cargo agents. Some items might be metered, for example fuel used for vehicles.
Logistic functions are supported using two applications Inventory Usage and Shipment Receiving. Inventory Usage is a document that can be used for issues, returns and transfers. It is an application that can be workflow enabled using Maximo’s built-in workflow capabilities, most Maximo applications can be workflow enabled. The Inventory Usage document can go through staging and shipping steps. Staging is used when items are collected together and added to a staging bin waiting to be collected. Shipments are used with transfers and create a shipping record which is then received into the destination storeroom using the Shipment Receiving application. Item availability is provided throughout Maximo wherever an item field exists providing the balances whether they are in a storeroom, staged or shipped.
Procurement & Contracts

There are four main applications in the Contracts Module. The Purchase Contract application is used for purchase, price and blanket contracts. When an item is raised on any of the purchasing applications Maximo will identify whether it exists on one or more active contracts. These are the types of contract that use the Purchase Order and Receiving applications.
The Lease/Rental Contracts application is used with assets which are leased or rented from a vendor. The main difference between the two is that a lease contract has options for returning or buying the asset at the end of the lease period.
The Warranty Contract application also supports Service Contracts. These are both asset or location based. When a warranty contract is set up then a warning will be shown on the work order when the asset or its descendent assets is referenced. Service contracts can occur after warranties expire and can also be used on work orders.
The Labor Rate Contract application is used for defining the vendor rates for different crafts and skill levels including the ways that overtime rates will be calculated. This type of contract will require time being reported against a work order by crews or labor.
Each contract type has a set of properties and a set of terms and conditions. New contract types can be created that use specific properties or terms. There is also a Master Contracts application which can contain the terms and conditions that will apply to all contracts associated with it.
The procurement applications in the Purchasing Module follow the processes from requisition through to invoicing. Which of these applications are used depend on whether there is financial integration to an ERP or financial system and then the agreed interface points between those systems. Maximo comes as standard with inbound and outbound integration objects for the supply chain processes of Maximo whether as part of Inventory or Procurement.
Desktop Requisitions is a set of self-service applications for all users of Maximo. The principle one, Create Requisition, guides the user through the process of creating material reservations or ordering new parts or services. When the requisition has been submitted it will create storeroom reservations or inventory usage records waiting to be issued, and purchase requisitions or purchase orders for items needing procurement. Similarly a work order will create inventory or purchasing demand when it is approved.
The Purchase Requisition (PR) and Purchase Order (PO) applications are similar, centralised purchasing is supported on the purchase order. Both have multiple lines which may indicate that a contract exists for the items, both can reference a contract in the header in which case the selectable items are those that belong to the contract.
The Request for Quotations (RFQ) application is used to obtain quotes from multiple vendors. PR lines are copied to the RFQ and as quotations are received the prices are entered. Vendor and item analysis can then be performed to determine how the RFQ will be awarded and one, many or all RFQ lines are then copied to a PO or contract.
The Receiving application is used to receive material or service lines against a PO. The receipt of materials can require inspection and if it is an asset then the serialization process will create the Maximo asset records.
The Invoice application is where financial transactions flow through to an Accounts Payable ledger in a financial or ERP system. In Maximo invoices may not have had an originating purchase order. Lease, rental, warranty, service and labor rate contracts can all generate invoices waiting to be matched to an incoming physical invoice from the vendor. Service based invoices can also be created directly in the invoicing application, for example where the vendor works from site and the authority to spend is on a work order, the vendor may only have a master framework contract in this case.
Financial Management & Analytics

Financial Module
Throughout Maximo financial transactions can be controlled against general ledger (GL) accounts that are set up in the Charts of Accounts application. These may be interfaced from an ERP or financial system. The GL account is made up of multiple segments and each segment has a set of values and descriptions. There are defaulting rules to derive the GL account on both the debit and credit sides of a financial transaction and where the GL account is not complete a navigator is used to help the user select the right codes. Financial transactions are also posted against financial periods. This all exists at Maximo’s organization level, it is therefore possible for Maximo to service multiple ERP or financial systems. The organization supports two base currencies and transactions may need to use the effective exchange rate, also held in Maximo.
Maximo has a Budget Monitoring application for setting and monitoring budgets against estimates, commitments and actuals. This is not limited to budgets set at GL account or GL segment level but may be set for a location, or asset. The Cost Management application supports integration from a financial system that has a projects ledger. The cost management records normally represent work breakdown structure elements and will be selected on the top level of one or more work orders that represent a work package. Maximo also supports asset depreciation schedules.
Analytics Module
The Maximo Start Center is an operational dashboard with tools for configuring it. There are several portlet types. The result set portlet utilises queries created in Maximo applications to fetch a set of records and this can also be pictured in pie or chart form. The KPI list or KPI graph portlets display the results of one or more KPIs using traffic light colours to represent a warning or action. The KPI can also be generated as a result of a query. In the KPI Manager application a KPI can be scheduled to run at a chosen frequency or immediately and the value recorded will be maintained in history so that a trend is created. The trend of multiple KPIs can also be viewed for comparison purposes. The KPI Templates application is used to generate multiple similar KPIs that differ only by the values selected and a KPI Viewer application can show all of a user’s KPIs in one colour coded list, ideal for using from a browser on a smartphone.
Maximo is supplied with a wizard driven ad-hoc report writer, this is an end-user’s tool for generating a listing or detail type report, it is not possible to generate graphical reports using this tool. The standard set of Maximo reports is created using BIRT, these are mostly analytical based. The Maximo Report Administration application provides control over security and performance, for example defining limiters or setting the schedule when a report will run. It is where report parameters are defined, which lookups and default value will be used, it is also the application where the report request page is generated. Reports can be saved and distributed as PDF or viewed from a Start Center portlet or from the Report Viewer application.
A Maximo license entitles the owning organization to download and install Cognos 11 Analytics for use with the Maximo data. This allows power users to create their own analytics and dashboards and to do this iteratively testing the output with stakeholders at each step – a term that is called agile analytics. Cognos Analytics supports descriptive, predictive and prescriptive analytics. There is also a Cognos Analytics mobile application. There is a Maximo application for designing data sets and a Work Center aimed at the Business Analyst.
Service Management & Service Level Agreements

Maximo provides service desk functions with the Service Request (SR) application, an SR is a type of ticket. The SR is classified and this is used to provide additional questions related to the type of service being requested. The service request can spawn one or more work orders which are handled in the Work Order Tracking application and there are multiple options for how a work order is created from the SR. Incidents are often handled in the SR application, although clients who use the HSE add-on will also be entitled to use the ITIL based Incident and Problem applications. Tickets and work orders can be related to each other. Tickets can also be deemed global, for example several people call-in to report that lights have gone out in an area.
SRs can be reported from a self-service application available to all users or integrated into the company portal. Maximo also has an email listener which would allow requests to be raised by email and automatically transferred to create a SR. Common service requests and incidents can be better supported through a ticket template which should reduce the processing time of a service request by at least 50%. These common requests can be made available to users to make the creation of a service request as painless as possible.
Complex requests may have multiple activities where those activities can be defined to run serially or in parallel. Ownership at group and individual level is tracked for both the SR and the activities. A user can always see the work they need to respond to whether tickets, activities or work orders through the Work View application and this is where work queues are defined.
Service Level Agreements (SLA) can be applied to the ticket, work order or activity. This calculates target dates for each record based on the commitment. SLAs are monitored through an escalation which can raise a notification if an SLA breach is approaching. The performance of an SLA can also be monitored over time using a Key Performance Indicator (KPI). SLAs can be applied to many types of record, not just those commitments which will result in the calculation of a target date.
Service Management extends across both tickets and work orders. Email communications can be generated to keep the originator and other stakeholders abreast of the service request or incident. Log notes added to a work order will be visible from the originating ticket and can be made visible to the originator of the service request. Status changes on follow-up work can update the status on the originating ticket. Tickets and work order records have similar functionality and are closely tied.
A solution is where a knowledge base would be established and are searchable by all Maximo users. Solutions can be applied to Incidents and Problems.
Planning & Scheduling (Scheduler)

The Planning and Scheduling module has the applications provided by the add-on products Maximo Scheduler. Planning aspects are performed in core Maximo applications the principle one being Job Plans, you will need to plan work orders to make an effective use of the Scheduler applications. All the scheduling applications are graphical and functionally rich.
The Graphical Scheduling application is for long to short term planning, there is a Gantt chart with histogram below showing the resource loading versus availability for the work orders included in the Gantt chart. Short term planning is best handled by using a rolling project where the work queries pull in work orders scheduled within the next 2-4 weeks. Graphical Scheduling will include the resource requirements of PMs without generating the work orders and will also support the scheduling of work for a set of locations or assets. Network dependencies are added between work orders or tasks allowing the critical path to be shown, float is also calculated. The Graphical Scheduling – Large Projects application might be used when the number of work orders goes above several hundreds and would be used for outages and shutdowns.
The Graphical Assignment application is for short term planning, typically within 2-3 weeks and the assignment of labor and crews to the work order assignments, it has three views. The Work View and Assignment View are both Gantt chart based, a supervisor would use drag and drop functions to assign the labor or crews to the work assignments. The Dispatch View shows the labor and crews assignments visually on a day calendar and map, it takes into account the travel time between work assignments. Using Maximo’s location-based services the latest geographic position of the labor or crew can be displayed along with new emergency work that needs assignment. The dispatcher graphically reassigns work to meet the new demand and street level routes for the labor and crews can be recalculated. With integration the dispatcher can see where there are weather alerts.
The Graphical Work Week application is used for scheduling and assigning work with a focus on the current week, or the next. It shows a Gantt chart of work assignments with a table of remaining hours for each Labor and Crew below. You can easily change availability by double-clicking in a resource cell and entering a reason code, holiday, sick, extra time, etc. Reason codes show up as a different colour. An assignment is also made by double-clicking or using selection boxes. Each resource shows the percentage allocation for the week. Assignments can be emailed or exported to a calendar (.ICS).
The Graphical Resource View application is focused on planning the availability of your Labor and Crews. It is a monthly calendar table with the resources as rows, each cell showing the shift that the labor or crew is working making it easy to see shift rotations. Holiday, sick, or extra time can be assigned across multiple days with a few clicks. Each reason code shows up as a different colour. Training can also be booked for multiple persons with a few clicks. No need to use a spreadsheet or wall planner to plan vacation schedules.
The Graphical Appointment Book application is normally used by a service desk to make appointments against fixed time slots during the day. Notifications are made to confirm the appointment, a reschedule, a cancellation or the estimated time of arrival. With integration the service desk can use weather data to help minimise cancellations and rescheduling.
The Graphical Assignment Repair Facilities application is also used for short term planning and assignment. A repair facility is used by transportation assets and might be a garage, railway shed, shipyard, or airport hangar. The repair facility is a location and it has a number of slots or bays where work is performed on the mobile asset. A work order can be assigned to one or more repair facility bays and labor or crews assigned that work at the repair facility.
The Graphical Crew Management application is used to assign labor to crew positions which require a type of craft. This is for week ahead crew management taking into account the unavailability of labor due to holidays, and the day to day management of the crew for short notice absences due to sickness and other reasons.
The Maximo Scheduler Optimization add-on is used with Graphical Scheduling and Graphical Assignments applications. It is an optimization engine the performs resource levelling, capacity planning, automated assignments including taking into account geographically dispersed work and there is also a model for handling the emergency work scenario, reworking remaining assignments to accommodate the new priority work.
Work Management

All types of work are planned, assigned and completed in the Work Order Tracking application. A template for a work order can be defined in the Job Plans application. A job plan can also have a nested job plan which when applied to a work order creates a hierarchy, ideal for a small project. Dynamic job plans flex the resource requirements depending on the number of work units to perform. Job plans are applied to Preventive Maintenance records which generate work orders performed at a time or meter frequency. A different job plan can be applied depending on which work order will be performed in the cycle, for example a quarterly job and a yearly job that includes the activities performed every 3 months. Seasonal based PMs are also supported, to avoid PMs on critical equipment being made during busy periods.
Inspections, including the capture of measurements or observations, can be handled through job plan tasks. A Route defines the set of locations and assets that will be visited as part of the inspection, each route stop can have a different job plan. Inspections can also be scheduled to run periodically. A wider range of inspections can be handled by the Manage Inspection Forms and its companion Conduct an Inspection work centers. SetsA set is used to share data across the Maximo Database. There are two types an Item Set and a Company Set. More of inspection questions can be dynamically added depending on the answer to a previous question.
Reactive and emergency work orders can be created from the Service Request, from the location and asset records or directly in the Work Order Tracking application. Work is planned by identifying the sequence of activities, and the labor (craft and crew types), materials, services and tools needed to perform the work or a task. On approval of the work material reservations will be placed and purchase requisitions created for non-stocked material and services.
Work is assigned to individuals or crews. A crew has required crafts, tools and qualifications that are needed to perform work, and labor are assigned to crew positions for a period of time. When making these assignments you can see whether the required crafts, tools and qualifications have been met and also whether the labor and crews is available in the same shift as when the work will be performed. The current geographic position of the individual or crew can be shown on the work order’s map tab using Maximo’s location-based services.
There is a desktop application called Quick Reporting which is designed for technicians needing to complete the work which has been assigned to them, this also allows them to report work which they did while on site which may not have been planned. When completing work, actual time, materials and tool usage is recorded, meter and measurement values are entered, and if relevant asset downtime and failure reports made. It is the comparison of the plan versus the actual which is important during work management.
Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)

The Health, Safety & Environment add-on is a suite of applications that significantly extend the footprint of Maximo. There are 31 new applications and extensions to 19 applications found in core Maximo. They will help a Maximo client who is working towards compliance with the ISO 55000 standards. The Oil & Gas Industry Solution has the same set of applications but also has ISO 14224 Classification and Failure data and a couple of other applications.
Policies and Procedures The three applications Regulatory Compliance, Operating Policies and Operating Procedures are used across many of the other HSE applications. External and internal regulations are used on both policies and procedures, Operating Policies are generally implemented on a work order. The audit part of the Audits and Surveys application is used to verify that the regulations, policies and procedures are being complied with.
HSE Incidents can be reported from a Maximo Anywhere mobile application or through a desktop application with similar functionality. The Incidents application would be used to record an injury/illness, a safety, environmental or security incident, a near miss, a spillage, a safety observation or a failure in a safety process. The Investigations application determines the root cause of the incident and corrective and preventive actions are created and monitored through the Action Tracking application.
The HSE applications support Operations Management. The Log Book and Operator Logs are used for shift logs and to aid shift handovers, but they can also be used for commissioning logs and monthly engineering logs. Operator Tasks are set by maintenance and performed by operators. The Benefits and Losses application is used to support both benefit identification and loss reporting and the Bypass Management application is used for evaluating and mitigating the risks associated with bypassing safety critical assets in order to perform maintenance or repair.
Control of Work provides process control and safety procedures when work is performed. It includes hazard identification, risk assessments, permit to work and isolation management. Permit to Work and Isolation Management are similar, but Isolation Management has a focus on the creation and life cycle processing of the isolation certificate needed for mechanical, electrical and process isolations of assets and operating locationsA location with a location type of OPERATING. More.
Management of Change. A Defect is used for recording issues with assets that may either need to be investigated, corrected by creating a work order or deferred to an outage or shutdown. An improvement is used for understanding the benefits of undertaking a project. Standard Actions and Standard Action Groups are used in many HSE applications for creating a checklist or a question/answer style list called Review Actions and are used at different stages in the MOC (Management of Change) application. There is an MOC Request application for organizations who would like any user to initiate a change.
HSE extends many core Maximo Asset and Work Management applications to provide a common thread between production, safety, quality and maintenance. The Locations and Assets applications allow failure modes and effect analysis (FMEA/FMECA) to be performed. The Certifications application is used for both certificates and permits, for example recording material certificates or certificates gained by people, for regulatory permits and environmental consents. The Condition for Work application can be used in conjunction with the Reason for Work and location/asset criticality to form a Prioritization Matrix which can drive the priority of work orders. The Work Order Tracking application has been extended to support turnarounds, construction or commissioning activities, for example, preparation activities, permits and certificates, and test results.
Mobility

There are three mobile products from IBM associated with Maximo. Maximo Anywhere is the only one which provides disconnected working. Maximo Everyplace and Maximo Work Centers are both browser based and work in connected mode only.
Maximo Anywhere applications work on IOS, Android and Windows, and can be used with smartphone or tablets. There are currently more than 10 applications, some are provided with the Industry Solutions, for example with HSE there is an Incident Reporter mobile application.
The main mobile applications are set around Asset, Inventory and Work.
- For Assets there is an asset data collection application and one for tracking down mobile assets at a location, Asset Audit.
- For Inventory three applications support; issues and returns, transfers and receiving and an application for physical counts.
- For Work there are applications for the supervisor, Work Approval, and ones for the technician, Work Execution and Inspection. There is also an application for creating Service Requests.
These applications are an extension of Maximo functionality onto a mobile device and have the expected functions that you would see in the desktop based applications.
In addition to these mobile applications Maximo Anywhere has a desktop administration application which controls the data and lookup queries used by each application and security group. Maximo Anywhere applications are built into the security framework of Maximo. Some Maximo Anywhere applications support online and offline maps. GPS Tracking and Push Notifications are used to notify a user about assigned work, for example, when they have been reassigned to work on an emergency work order. Error checking ensures that Maximo data validations are being maintained. Mobile instrument calibration is supported with an extension to the Maximo Anywhere Work Execution application.
Maximo Everyplace is browser based and works in connected mode only, there is no offline capability. The default applications are work order based one for a Supervisor and the other for a Technician. Configuration is performed using Application Designer, the same application used for configuring Maximo desktop applications. An existing Maximo application can be converted to a Maximo Everyplace application by cloning it (copying it), marking it as a mobile application, which will make the buttons larger, then removing fields and moving others around to fit the size of the device.
Maximo Work Centers were first released in June 2016 as part of the 7.6.0.5 feature pack and they have been enhanced and added to frequently since then. I will discuss these on a separate page.
With Maximo 7.6.1.2 there is the entitlement to download and use Cognos Analytics 11.0.13. This is the on-premise version only. There is a mobile application for Cognos Analytics.
Asset Health, IoT & Predictive Maintenance

Maximo Asset Health Insights (MAHI), now called Maximo Health, would be used by reliability engineers to gain visibility of the health of assets and locations. Factors like condition, performance, costs and remaining useful life enable you to monitor assets to prevent their failure. If you are more aware of an asset’s health then you may use this information to adjust preventive maintenance or inspection schedules or make repair or replacement decisions.
In Maximo Health you use scoring methods created using Maximo Formulas to derive a health score for the asset and location. A reliability engineer creates multiple drivers for example condition, cost, etc, and then for each driver one or more factors, for example measurements and observations could be factors for the condition driver. Each factor and driver can have a weighted value. Health scores are calculated against the assets and the lowest health score is shown on the location and up the location hierarchy to the top. Health scores can be updated using background cron tasks. As a reliability engineer I can subscribe to notifications on assets to define what situations I want to be notified of, and how I want to be notified, within Maximo or by email or SMS.
Failure history and the preventive maintenance schedules of assets can be used with an integration to IBM Predictive Maintenance, now called Maximo Predict, a cloud based predictive model for determining the next predicted failure date. This would require a license to use IBM Predictive Maintenance. This application will also indicate whether your PMs are being performed too frequently or too infrequently and by how much.
SCADA data, sensor data or data already collected in data historians like OSI PI, can be collected through IBM Watson IoT Platform and used to monitor asset conditions and trigger actions based on the change of data. This is now wrapped up in a product called Maximo Monitor.
The sensor data associated with an asset at a location can be visualized on a map for geographically dispersed assets. If a client has license to IBM IoT Weather Data on Cloud they can access historical, current and forecast weather, as weather can be a factor in asset life. If a client has the Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) add-on then they can investigate and reduce asset risks from the Risk Reduction tab. This is a view onto the open investigations made from the Reliability Work Center.
Maximo Work Centers

Work Centers is a modern role-based user interface that is responsive to the device whether desktop, tablet or smartphone. They are based on HTML5 and web component technology. Each work center is focused on the action which the user is taking, they only provide the fields which are necessary to perform that action, which makes the user interface easier to learn.
The main work centers support Service Requests, Work Orders, for both the supervisor and technician, Inspections, Inventory, and also one for Administration. The work centers are further ahead on the Maximo EAM SaaS version, as they have frequent new releases. For existing Maximo clients and on-premise new clients there is currently a new release each year. Maximo Health (MAHI) uses the work center technology.
Currently, the work centers only operate when the device’s browser is in connected mode, there is no offline capability, yet. There is also limited configuration capability, but we know from the Maximo roadmap that the IBM team are working to move work centers to work offline and also to provide configuration capability. It is also understood that working offline will require a Maximo Anywhere license.
Maximo Configuration

Maximo has a rich configuration toolset. All configurations are stored in the Maximo database and are mostly maintained during an upgrade, a utility will need to be used to migrate screen changes.
Maximo has its own Workflow engine and workflow processes can be enabled on any Maximo application. The Task nodes make the assignments to people or person groups, a role is used to make these assignments dynamic. The assignments may send an email using a Communication Template or the user might monitor their workflow inbox for the assignments they need to perform. Workflow may also perform actions which might change status, set a value, perform an application action, for example apply an SLA, or execute a custom action written in Java or a script. The Escalations application uses some of the same elements as workflow but this is based on monitoring the database for a condition to occur and then performing a set of actions and notifications in the background when it does.
The Database Configuration application makes changes to the object layer and their underlying data tables, views can also be created. This is the application where you define electronic records (auditing) and electronic signatures (confirming who you are), and where you create formulas and associate them with objects or attributes. It is also the place where the relationships between objects and all messages are defined.
The Application Designer application is where you can modify the user interface (UI) of the application, its dialog boxes, the actions, toolbars, lookups, menus and hover-over dialog boxes. Each of the UI elements can be bound into the security layer of Maximo and set to conditionally display or conditionally change its properties, for example, hide or display a set of fields when a condition is met, display text in red when it is an emergency work order.
The security framework is controlled through the Security Groups application. A user belongs to multiple security groups and each security group builds up a layer of security. The security group provides access rights to Maximo applications and their actions, Start Centers, Storerooms, GL Components, Labor, and Integration Objects. Data security can be controlled at the record or attribute level.
The Domains application defines sets of ALN and Numeric values which are used with lookups. Numeric Range Domains are used to set a range of values, for example a percentage between 0 and 100 to 2 decimal places. A Table Domain creates a set of values that can be defined by a query from other data in Maximo and a Crossover Domain does something similar but then copies data from the source object record to the current record. For example, a crossover defines what is copied from the service request when a work order is created.
Migration Manager is a set of applications used to control how configuration data is transferred between the development, test, and production environments. It also migrates some other low volume data but not all data in Maximo can be or should be migrated using Migration Manager, it depends on the complexity and volume of the data.
Customization is performed by extending Maximo’s Java classes or developing Automation Scripts. There are advantages and disadvantages with each, but whichever is used this is the area which should be tested most when upgrades to Maximo are provided. IBM’s policy towards extending the application and feature set of Maximo is to do this incrementally, with release of feature packs, roughly once per year. For the last seven years the policy has been to add new functionality without changing the existing data. Customization will also be mostly handled as part of an upgrade unless the new Maximo functionality cuts across your custom code. Customization isn’t wrong as long as it is contained to reasonable levels. The more customization you have the more regression testing should be performed.
The Integration module has a comprehensive suite of integration applications, both inbound and outbound. Data loading is also performed through the Maximo Integration Framework (MIF). The most recent addition allows Maximo’s application business objects to be made available as REST resources for queries and updates of application data by external applications. Maximo comes packaged with many pre-defined object structures which is the starting point for integration points.
The IBM team continue to enhance the set of tools used by developers and administrators. For example, there is a License Usage Monitor, a Management Interface for monitoring the performance of Maximo and a utility for anonymising personal data in order to comply with recent regulations. IBM continues to update the platform components to remain current with database, operating system and browser versions.
Trends in Enterprise Asset Management

Now, that we have introduced Maximo, what are the trends we are seeing in Enterprise Asset Management?
Industry 4.0 is termed the 4th industrial revolution and originated from an initiative by the German government to ensure competitiveness in manufacturing industries. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is another term meaning the connection of sensors to the Internet with a focus on manufacturing and industrial processes. It is the expected rapid rise in the number of these sensors which is coined as big data.
Enterprise Asset Management now has two standards PAS55 and ISO 55000 and these have extended the boundaries beyond asset, work, inventory and procurement the traditional areas of maintenance management systems (CMMS). For example, management of change, risk assessments, performance monitoring and continuous improvement are all included. A good document to read is from the Institute of Asset Management – “Asset Management – an Anatomy”, which has been aligned with ISO 55000.
But there are other trends which are influencing the direction of Enterprise Asset Management.
- Mobility, not a new subject by any means, but the user interface for desktop and mobile applications is converging, a mobile worker wants to be able to do more than record an asset or complete a work order, wireless communication is becoming more prevalent and cellular technology is moving towards 5G which is the enabler for the connected world. The world of mobility is changing.
- Advanced Analytics are needed in order to make sense of all the big data being collected and to make it easier to digest by business users.
- Descriptive Analytics, answers “What has happened?”
- Predictive Analytics, looks to the future and answers “What could happen?”
- Prescriptive Analytics, evaluates possible outcomes and answers “What should we do now?”
- Worker Safety covers both wearable technology, sensors that monitor a workers health and wellbeing, as well as proximity safety, tracking a worker who has entered or is approaching an unsafe area.
- Drones is one form of visual inspection but there are other types with fixed or mobile camera where the change in an asset can be identified over time through photographic evidence
- Augmented Reality is a technology that superimposes a computer-generated image on a user’s view of the real world, thus providing a composite view.
- Cognitive Services are a set of machine learning or deep learning algorithms that solve problems in the area of Artificial Intelligence
- Blockchain is a transparent, secure and tamper-proof digital ledger that can track different types of data in private blockchain networks which are shared between different stakeholders.
Maximo Investments and Innovation

We saw that there are a number of trends in Enterprise Asset Management. The AI Applications division of IBM, which is where Maximo resides, is working and has products in all of those areas, and part of the Maximo investment strategy is to leverage those products providing tight integration with Maximo. Comparing to the roadmap from 18 months ago, much of this has been done with additions to the APM portfolio, the second step will be to move all products together onto a common platform – Maximo Application Suite, that project has already started.
IBM regularly publishes a Maximo roadmap, roughly twice a year. This slide shows the main areas of investment expected for Maximo over the next couple of years – this slide was published in July 2020. As with all roadmaps please read the IBM note at the bottom of the screen, as the plans, directions and intent are subject to change.
- Maximo 7.6.1.2 has just been released and includes a number of enhancements to Work Centers, Inventory support for hub and spoke storerooms, a new location/asset drilldown, and ability to create multiple document attachments in one action. Asset data can also be imported from IBM’s new Digital Twin Exchange.
- Persona Based Experience is implemented by Maximo Work Centers. The Maximo 7.6.1.2 release had a number of enhancements, mainly in Inventory including picking and staging, reconciling inventory balances, support for item condition codes, and support for barcode and QR code scanning. On the work order based work centers you can now launch an inspection, classify a work order and view a URL to a web page. On the Work Supervision work center there is support for crew assignments. In the Work Execution work center meter readings can be recorded for the multiple assets and locations referenced on the work order. The Service Request tool can now be accessed by guest users. There are many more enhancements across these Work Center applications than can be referenced here.
- Industry Solutions and Add-ons.
- Civil Infrastructure is the newest Industry Solution to be added to Maximo. It is for bridges, roads and tunnels. At its foundation it looks to be a combination of core Maximo, Linear, Spatial, BIM, Monitor, Predict and the Visual Analytics from Drone surveillances.
- Maximo Scheduler 7.6.8 is a significant new release including three new applications, Graphical Work Week, Graphical Resource View and Scheduler Data Manager. The Scheduler Plus capabilities have been merged into Maximo Scheduler, giving users access to Graphical Appointment Books and Graphical Scheduling – Large Projects applications, and other features like progress reporting and an indication of the critical path. Access to the optimization capabilities now requires a separate license, this too has been reworked for CPLEX Studio based models.
- There has been a new release of Maximo for Aviation/ACM/SP, Maximo Nuclear and Maximo Utilities/Spatial/Linear. A new release of Maximo O&G/HSE is expected before the end of 2020.
- Mobility. The mobile products are currently Maximo Anywhere, the Work Centers, Maximo Everyplace and Maximo Assist, which extends the mobile applications with virtual assistance. There are four main areas of development:
- Maximo Anywhere. The first step for Maximo Anywhere has already occurred with the removal of the Mobile First component which simplifies the architecture and removes license restrictions allowing new apps to be created. There is a convergence of Maximo Work Centers and Maximo Anywhere and with this is a dependency on the ability to configure the Work Centers with visual configuration tools. The Work Centers are being moved to use IBM’s open-source design system, called Carbon and this is being used to create a Work Center Development Framework.
- Maximo Assist AI. This brings Artificial Intelligence to field teams allowing them to improve problem diagnosis by asking natural language questions to find recommendations based on ingested structured and unstructured data.
- Maximo Assist AR. This adds Augmented Reality to the mobile device and access to remote experts, an AR-enabled visual session, which can then be added to the repository of unstructured data used to provide assistance in the future.
- Maximo Worker Insights. This combines IoT data from wearables and environmental sensors giving visibility to hazardous conditions. It has integration to Maximo HSE Incident process. It will be called Maximo Safety.
- Maximo Application Suite (MAS). This is the pulling together of most of the Maximo family of products including the Maximo APM products into a single suite of applications (see next slide). Along with MAS is a new concurrent license model, based on the consumption of application points, and a committed term of 1 to 5 years. It will provide entitlement to the whole product suite with users consuming application points based on what they are accessing at the time.
- Modernization. All the products that form part of Maximo Application Suite will have the same look and feel based on the Carbon open-source design system which is being used for the reworking of the Work Centers. Maximo with all its Industry Solutions and add-ons has hundreds of applications, some of which are suited to use only on a desktop. I do not expect all applications to be converted but those which need to be used remotely should be candidates in future years. I will expect the core Maximo look and feel to be aligned towards the new look and feel, but not replaced by it.
2021 looks to be a big year with the coming together of the Maximo family of products in Maximo Application Suite under a new user interface.
Maximo Application Suite (MAS)

The operating models for asset intensive industries is changing, as we saw in the slide on trends in Enterprise Asset Management, Industry 4.0 and IIoT. There has been SCADA systems for many years and some clients will have integrated this to their CMMS perhaps via asset data historians. There is a growing demand to add sensors to assets to detect anomalies before the point where traditional control systems are designed to react. This is all in aid of improving assets reliability, to increase uptime for production, to extend asset life, and reduce operational costs. The sensors are creating a lot of additional data, and there are other sources of data, visual records from drones, or satellite images, real-time remote monitoring systems, etc. This is not the data we would expect to find in a relational database, and data is only as good as the analytics used to make sense of it.
The operating models for technicians is also changing and creating more data. Technicians have sensors embedded in wearables and personal protective equipment (PPE), for example, hard-hats, wearable bands designed to pick-up fatigue, smart watches, or their smart phones and tablets which also have an array of sensors. Technology is also changing what can be achieved through a smart phone or tablet. For example, the ability to have AI based assistants on those devices or to use the camera to connect with a remote expert, and to record those sessions and make them available for other technicians who may find themselves in a similar situation.
The Maximo product portfolio has been expanding over the last few years, with the Asset Performance Management (APM) products, but in other areas too. All of the components needed to take a Maximo client on the road to be able to predict failures are in place, but they need to be brought together under a single platform and license model to make it accessible. That single platform will be called Maximo Enterprise Suite, Maximo 8.x.
Maximo Enterprise Suite will combine the following products:
- Manage – Core Maximo but with the Industry Solutions and add-ons that you need
- Monitor – Allows you to move to condition-based maintenance with remote monitoring of your assets at enterprise scale and using AI-based anomaly detection to provide fewer and more accurate alerts.
- Visual Inspection – Train models to classify and detect objects in images and videos using computer vision. Visually detect anomalies.
- Scheduler – Maximo Scheduler, scheduling and assigning work and resources
- Mobile – Maximo Anywhere, online and offline applications for the technician; work, inventory and asset data based.
- Assist – Prescriptive guidance on the most effective repair – Equipment Maintenance Assistant
- Health – Asset health scoring and assistance in making repair/replace decisions – Maximo Asset Health Insights (MAHI).
- Predict – PM optimization and prediction of next failure date – Predictive Maintenance Insights.
- Safety – Integrates sensors in wearables to monitor employee wellbeing, also proximity safety – Maximo Worker Insights.
For asset intensive industries you might say that you cannot have AI without a digital twin. Data about your assets both structured and unstructured is a key to success in being able to move forward in your asset management maturity journey. The Digital Twin Exchange provides the digital footprint needed to be able to predict failures when coupled with your operational data. This is more than a 3D representation of your assets, a simulation twin, but all the digital information you need to own and operate your business effectively. It is not a unified view of your plant, because often you do not have all of this data, but you can have digital twins for many of the assets in your plant.
The Digital Twin Exchange is a platform that allows manufacturers, OEMs and third parties to share their digital resources. Bill of materials, parts list, user manuals, failure codes, maintenance plans, stocking strategies, BIM models, 2D/3D CAD files, AI models, etc. It is open for business and with Maximo 7.6.1.2 there is a new action for importing this asset data directly into Maximo.
Maximo Enterprise Suite will be a single integrated platform, designed for enhanced data sharing. It will have a multi-cloud and hybrid deployment, built on the RedHat OpenShift Container Platform, optimised for scale and available for deployments on-premise, private and on public clouds.
There will be a simplified licensing model, a user can access any of the products in the suite. It will be a concurrent license model where each user consumes application points depending on which parts of the suite they are using at the time. It will not be a perpetual license, but one based on a committed term of 1 to 5 years.
Maximo Application Suite was announced on 29-May-20 and release 8.0 and 8.1 have been delivered. This includes the components of Monitor, Health and Predict, all using the same Carbon-based user interface. The latest roadmap shows a release per quarter with Visual Inspection next on the list and Manage being added in Q1 2021 (subject to change).
The IoT Community for Maximo is probably the best place to monitor for new events – https://community.ibm.com/community/user/iot/communities/community-home?CommunityKey=3d7261ae-48f7-481d-b675-a40eb407e0fd
Other useful links are:
Maximo Application Suite https://www.ibm.com/products/maximo
Manage https://www.ibm.com/products/maximo/asset-management
Monitor https://www.ibm.com/uk-en/products/ibm-maximo-asset-performance-management/asset-monitor
Visual Inspection https://developer.ibm.com/components/maximo-visual-inspection/
Assist https://www.ibm.com/products/maximo-equipment-maintenance-assistant
Health https://www.ibm.com/uk-en/products/ibm-maximo-asset-performance-management/asset-health
Safety https://www.ibm.com/products/iot-safer-workplace and https://www.ibm.com/business-operations/enterprise-asset-management/worker-workplace-safety-solutions
Maximo Production Optimization https://www.ibm.com/uk-en/marketplace/production-optimization
Maximo APM from Energy and Utilities https://www.ibm.com/uk-en/products/ibm-maximo-asset-performance-management/energy-and-utilities
Maximo continues to lead in EAM

Finally, Maximo continues to maintain a leadership position in Enterprise Asset Management as it has been recognized by industry analysts Gartner, IDC and ARC Advisory Group for more than the last decade.

Thank you for listening